What is a Web Proxy?
In today’s digital world, privacy and security are essential concerns. Whether you’re browsing the web or accessing online services, ensuring that your online activity is protected has become a necessity. This is where web proxies come into play. If you’ve ever wondered what a web proxy is and why it matters, this guide will give you the complete rundown.
In this article, we’ll explain web proxies in detail, how they work, and when they are useful. We’ll also compare different types of proxies and weigh their pros and cons. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of whether a web proxy is right for your needs.
What is a Web Proxy?
At its core, a web proxy acts as an intermediary between your device (computer, smartphone, etc.) and the internet. When you use a web proxy, instead of your device directly interacting with websites, the proxy server handles the communication. This masks your IP address and can provide several benefits like increased privacy, anonymity, and access to blocked content.
How Does a Web Proxy Work?
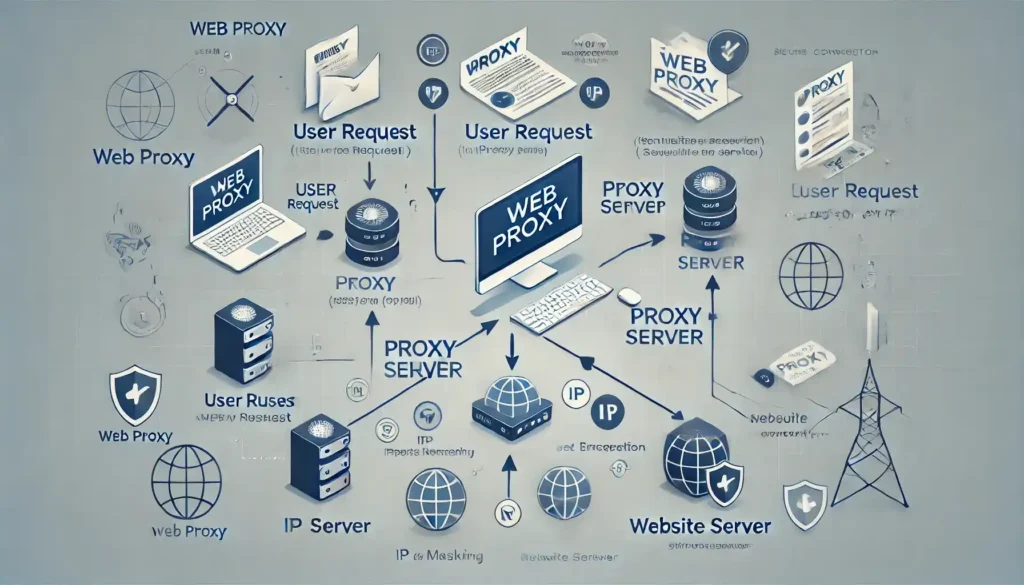
Here’s how it typically functions
- You connect to a web proxy server by configuring it in your browser or using a specific proxy service.
- When you request access to a website, instead of going directly to the site, the request is routed through the proxy server.
- The proxy server sends your request to the destination website, retrieves the information, and then forwards it back to you.
The key advantage here is that the destination website only sees the proxy server’s IP address, not your actual IP address, which helps enhance privacy.
Web Proxy ?
To better understand the role of a web proxy, let’s break down its process visually:
[How a Web Proxy Routes Requests]
- User → Proxy Server → Website.
- The website responds to the proxy server.
- The proxy server then forwards the data to the user.
Key Points
- A web proxy helps hide your IP address.
- It acts as an intermediary, keeping your identity anonymous.
- It can filter and block certain content or websites based on predefined rules.
Types of Web Proxies
There are several types of web proxies available, each offering different functionalities. The three main types are HTTP Proxy, HTTPS Proxy, and SOCKS Proxy. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Type of Proxy | Definition | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP Proxy | Works only for web traffic | Ideal for browsing and web scraping |
| HTTPS Proxy | Supports encryption (SSL) | Secure websites, online transactions |
| SOCKS Proxy | Versatile for different traffic types | Torrenting, email, FTP |
HTTP Proxy
The HTTP proxy is the most basic type of proxy and only works with websites that start with “http://”. It routes web traffic from your browser to the desired website, making it suitable for browsing and web scraping. However, it’s important to note that HTTP proxies do not encrypt your data, which makes them less secure for sensitive information.
When to Use:
- Non-sensitive browsing
- Web scraping
- Speed-focused tasks
HTTPS Proxy
An HTTPS proxy is an encrypted version of an HTTP proxy. It works with websites that use SSL certificates (those that start with “https://”). This makes it ideal for more secure browsing and for handling sensitive information like online banking.
When to Use:
- Secure online transactions
- Sensitive browsing
- Protecting personal information
SOCKS Proxy
A SOCKS proxy is a more versatile option that supports all types of traffic, not just web traffic. It works with protocols like FTP, email, and torrenting. However, SOCKS proxies tend to be slower compared to HTTP or HTTPS because they handle more complex tasks.
When to Use:
- Torrenting
- Gaming
- Accessing restricted content
Pros and Cons
Using a web proxy has several advantages, but it also comes with some drawbacks. Let’s break down the pros and cons in a quick table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provides anonymity by masking your IP | May slow down your internet connection |
| Helps bypass geo-restricted content | Free proxies can log and sell your data |
| Enhances privacy on public networks | Limited encryption compared to VPNs |
| Allows controlled access to blocked sites | Not all proxies offer strong security |
Pros
- Anonymity: Your actual IP address is hidden, making it harder for websites or services to track your browsing behavior.
- Bypassing Geo-restrictions: A web proxy can help you access content that’s unavailable in your region.
- Privacy: Web proxies add an extra layer of privacy, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Content Filtering: Certain proxies allow users to block or restrict access to unwanted websites.
Cons
- Slower Internet Speeds: Since your requests are routed through a proxy server, it can lead to slower browsing speeds.
- Logging Concerns: Some free or poorly managed proxy services may log your data and sell it to third parties.
- Limited Encryption: Unlike VPNs, most web proxies don’t encrypt your data, leaving it exposed to potential hackers.
- Not Suitable for All Applications: For activities like secure online banking, proxies may not offer adequate protection.
When Should You Use a Web Proxy?
Understanding when to use a web proxy is crucial for maximizing its benefits while minimizing its downsides.
Best Situations to Use a Web Proxy:
- Privacy and Anonymity: If you need to browse the web anonymously or mask your IP address, a web proxy is a simple solution.
- Bypassing Geo-blocks: If you want to access region-restricted content (like watching a show on Netflix that’s only available in another country), a proxy can help.
- Using Public Wi-Fi: Public networks are often insecure, and using a web proxy can add a layer of protection.
- Avoiding Censorship: In countries or workplaces where certain websites are blocked, a web proxy can give you access to restricted content.
Web Proxy vs VPN: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse web proxies with VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), but there are significant differences. Here’s a visual comparison to help clarify:
| Feature | Web Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Routes traffic via a proxy server | Encrypts all internet traffic |
| Security | Limited encryption or none | Full encryption |
| Anonymity | Masks IP address | Masks IP address + encrypts data |
| Speed | Faster, but limited protection | Slightly slower, higher protection |
| Use Case | Light browsing, bypassing restrictions | Secure browsing, torrenting, accessing sensitive info |
Key Differences:
- Encryption: VPNs encrypt all your internet traffic, whereas most web proxies don’t.
- Security: VPNs are more secure and reliable for protecting sensitive information.
- Speed: Proxies are generally faster, but VPNs provide higher protection.
Conclusion
A web proxy is a simple tool that offers privacy and can bypass content restrictions. It’s a good solution for users who want basic anonymity or need to access geo-restricted content without heavy security.
It’s important to note that while web proxies can offer a certain level of privacy, they may not provide the comprehensive security required for more sensitive activities such as online banking or sharing personal data. In these cases, a more robust solution like a VPN is recommended.
For everyday browsing, a web proxy is a convenient tool. It’s easy to use and can quickly provide the privacy you need. However, for more security-sensitive needs, a VPN is the better choice.
Key Takeaways
- A web proxy hides your IP address and routes traffic through a third-party server.
- Different types of proxies (HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS) are suited for specific tasks.
- Web proxies are great for anonymity, bypassing geo-blocks, and enhancing privacy on public Wi-Fi.
- VPNs offer more robust security through encryption and are better suited for sensitive activities.
Now that you’ve grasped the basics of web proxies and their comparison to VPNs, you’re better equipped to make an informed decision about your online privacy needs.



